A diode is a small electronic component which allows an electric current to flow in one direction only. A light-emitting diode (“LED”) is a diode that lights up when a current is flowing through it.
In this tutorial:
See also:
Definition
A diode is a small electrical component that only allows electricity to flow in one direction in a circuit. The cathode is the negative terminal, and the anode is the positive terminal; the diode is connected so that the charge flows from the (positive) anode to the (negative) cathode.
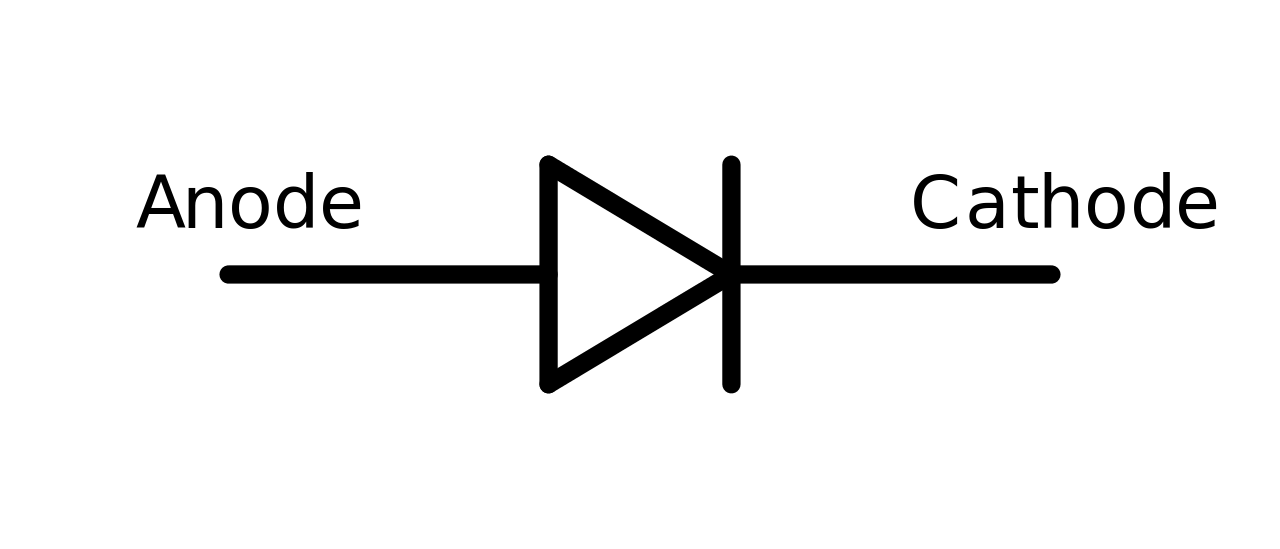


Uses
Diodes are found in rectifiers to convert alternating current (“AC”) to direct current (“DC”) as well as for demodulation in radio receivers.
LEDs are commonly used as electric lighting and status indicators on electronic devices. You will also have heard of LED screens for digital devices and computers.
A practical investigation
Equipment:
- 9V battery
- an old CPU Cooling fan
The cooling fan commonly found on a CPU can easily be removed from an old, defunct computer. Take one and connect it to a 9V battery. You will notice that the fan only works when connected one way in the circuit; reverse the polarity by flipping the battery, and the fan does not work.
If the fan did work, reversing the polarity would result in the fan spinning in the opposite direction, sucking air — and dust — onto the CPU instead of away from it.
To ensure the fan is always only blowing air away from the CPU, a diode has been used to ensure that it cannot be connected “backwards”.
Next steps
Coming soon:
- Electronics 101
- Breadboard basics
References:
- Robledo, E. (2024) How does a Diode and LED Work? Fusion Blog. Available at: https://www.autodesk.com/products/fusion-360/blog/diode-led-work/ (Accessed: 25 May 2024).
